Position: Resource - Partition Management - 7 Free Disk Partition Tools for Windows, macOS, and Linux
Make a backup for important data before you begin!
A disk's structure will be altered during partitioning, and errors, no matter how minor, can erase your data. Before making any changes to your hard drive, create a full backup of your important files. Having a backup is your best safety net against accidental data loss.
| Tool Name | Platforms | User Level | Highlights | Limitations |
| Disk Management | Windows | Beginner | Covers basic needs | Lacks advanced features |
| DiskPart | Windows | Advanced | Scriptable, powerful, built-in | High risk if used incorrectly |
| DiskGenius Free | Windows | All levels | Disk partitioning, data recovery | Windows-only |
| Disk Utility | macOS | Beginner | Clean UI, great for Mac users | Limited compared to diskutil |
| diskutil | macOS | Advanced | Command-line, good for automation | Command-line complexity |
| GParted | Linux | All levels | Powerful GUI, wide filesystem support | Requires boot media for system disks |
| parted / fdisk / mkfs | Linux | Advanced | Flexible CLI tools, great for servers | Steeper learning curve |
Windows Disk Management is the default utility for handling simple partitioning tasks. It's integrated into the system, which means no extra installation is necessary, and the interface is accessible through the computer management console. For routine tasks like assigning drive letters, resizing existing partitions, and creating new partitions, this partition tool is reliable.
While Disk Management, its capabilities are limited. It cannot merge unallocated space to a partition if they're not adjacent, nor does it support advanced recovery features. For users who want quick changes without third-party tools, it's the go-to option, especially in corporate or enterprise environments where tool installation might be restricted.
Key features include:
• Creating, deleting, and formatting partitions quickly
• Extending or shrinking partitions within contiguous free space
• Changing drive letters and mount points without rebooting
• Supporting common file systems: NTFS, FAT32, exFAT
• Initializing new disks for first-time use
Steps to create a new partition in Disk Management:
Step 1. Right-click the Start button and select Disk Management.
Step 2. Locate the unallocated space and select "New Simple Volume".
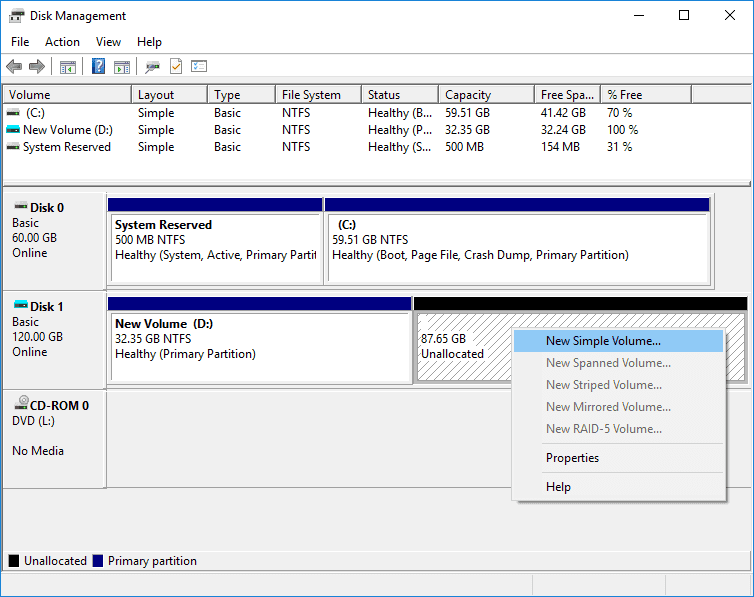
Tip: if there is not unallocated space on your hard drive, you can shrink an existing partition by right-clicking and choosing "Shrink Volume".
Step 3. Follow the partition wizard to specify size, drive letter, and file system. After that the partition will be created and formatted quickly.
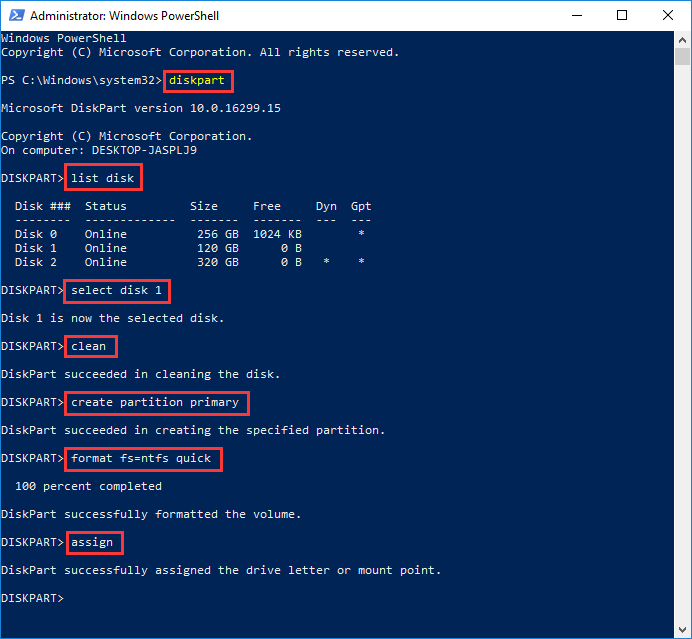
DiskPart is the more powerful, command-line counterpart to Disk Management, included in all modern Windows versions. It's favored by IT professionals and advanced users who require scripting capabilities or need to automate disk setups. Unlike the GUI, DiskPart enables batch operations and finer control over partition attributes.
That said, DiskPart demands caution. Commands like clean erase an entire disk without confirmation, and improper use can cause irreversible data loss. It's ideal for users who understand Windows storage architecture and need granular control over disk layouts, particularly in server environments or automated deployments.
Here's what you can do with DiskPart commands:
list disk (Display all connected disks)
select disk # (Choose a target disk for operations, # should be replaced with the correct number)
clean (Remove all partitions and data on the selected disk)
create partition primary (Create a primary partition)
format fs=ntfs quick (Perform a quick format for the partition with NTFS file system)
assign (Assign a drive letter for the newly created partition)
Note: DiskPart does not prompt for confirmation before destructive commands like clean, format. So, you should make sure you fully understand the consequences before executing such commands.
DiskGenius Free is a free third-part disk partition tool, and it combines partition management features with robust data recovery capabilities. It has portable versions for both 64-bit and 32-bit computers. With this tool, you can:
• Create, delete, format, resize, shrink, extend, and securely wipe partitions.
• Format a partition to EXT4, FAT32, exFAT, NTFS.
• Clone partitions and image partition.
• Clone a hard drive to multiple disks at the same time.
• Conver disks between MBR and GPT without deleting data.
• Migrate Windows OS to HDDs, SSDs, or USB drives.
• Completely wipe hard drives and make data unrecoverable.
• View SMART information for HDDs and SSDs.
• Check and repair bad sectors.
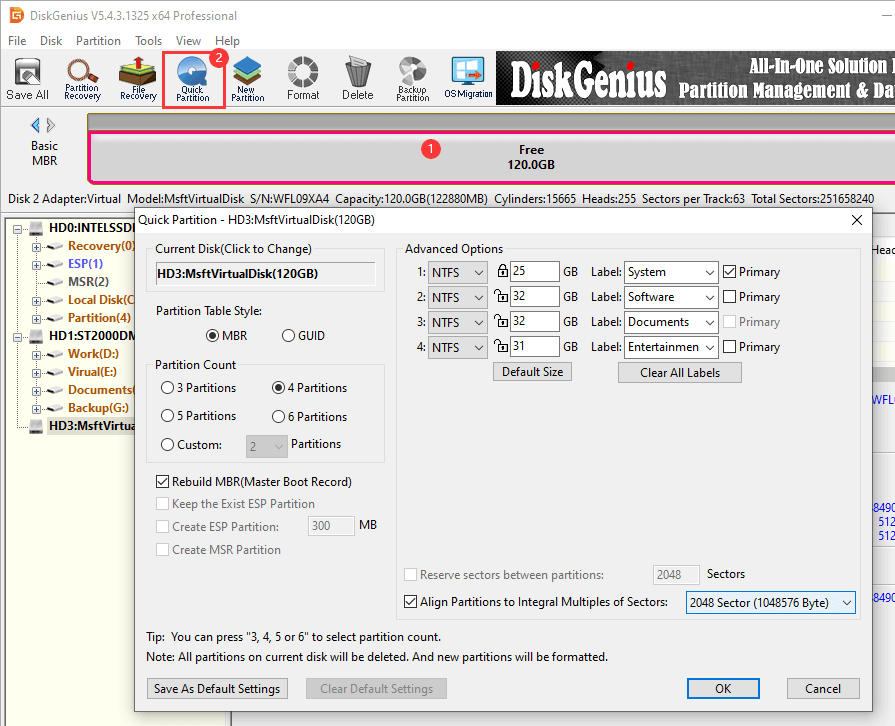
Here are steps to repartition a hard drive (Delete all existing partitions and quickly create new partitions):
Step 1. Select the hard drive you want to repartition and click "Quick Partition".
Note: Please back up all important files for the hard drive and keep backups on another hard drive, as the repartitioning process removes all existing partitions and data.
Step 2. Specify partition table type, partition count, size, volume name, file system, 4K alignment. Then click "OK".
Disk Utility is macOS's native and user-friendly disk management application, designed for simplicity and integration. Its clean interface caters to users who need to perform everyday tasks like partition creation, deletion, merging, and disk formatting without delving into terminal commands.
This tool supports both internal storage and external devices like USB drives. It's reliable for maintaining Mac file systems such as APFS and HFS+, but can also handle FAT and exFAT for cross-platform compatibility. Advanced users may find some limitations compared to command-line tools but for most Mac users, Disk Utility strikes the right balance between usability and functionality.
Features you often use:
• Create, delete, and merge partitions with drag-and-drop ease
• Format disks to APFS, HFS+, exFAT, and more
• Verify disk health and repair common errors
• Create and manage disk images for backups

For those comfortable with the command line, macOS includes diskutil, a comprehensive disk management tool offering capabilities beyond the GUI. It's suited for automation, scripting, or when troubleshooting requires command-line precision.
diskutil supports creating and resizing partitions, erasing volumes, and changing file system types, making it a vital tool for power users and administrators. It's especially useful for managing APFS containers, which can be complex to handle via Disk Utility.
Things you can do with this tool:
diskutil list (List disks and partitions)
diskutil partitionDisk /dev/disk2 GPT APFS NewVolume 100% (Partition a disk with a new APFS volume)
diskutil eraseVolume APFS "NewDrive" /dev/disk2s1 (Erase and reformat a volume)
GParted is a graphical, open-source, and cross platform tool, popular in Linux distributions but also usable via Live CD or USB on other OSes. Its features include resizing, moving, and repairing partitions, making it accessible for both novices and advanced users.
One of GParted's strengths is its extensive filesystem support, including NTFS (Windows), FAT32, ext4 (Linux), and Btrfs, among others. Running GParted from a bootable media allows you to modify system partitions safely without interference from running OS processes.
Here's what it can do:
• Resize, move, create, and delete partitions with visual feedback
• Supports most common filesystems, including Windows and Linux formats
• Check and repair filesystem integrity
• Fix partition table issues and recover lost partitions

Power users and system administrators often prefer command-line tools on Linux for their flexibility and scriptability. These tools offer granular control over disk partitioning, filesystem creation, and maintenance.
fdisk: Classic utility for creating and modifying MBR partitions. It's widely supported but limited to older partition tables.
parted: More modern and versatile, supporting GPT and MBR. Suitable for disks larger than 2TB and more complex partitioning schemes.
mkfs: Used to create filesystems on partitions (ext4, xfs, FAT32, etc.).
lsblk and blkid: Utilities to inspect disks and partitions.
fsck: Filesystem consistency checker, used to repair corrupted filesystems.
Disk partitioning isn't just a task for IT specialists, it benefits everyday users too. Whether you're installing a second OS, managing limited storage space, or organizing your personal data more efficiently, partitions can make your system cleaner, faster, and easier to maintain. Here are some cases for disk partitioning:
Managing disk space: Windows and macOS tend to fill up over time with apps, updates, and temporary files. Creating a separate partition for your personal files helps free up system drive space and improves overall performance.
Dual-boot or Multi-OS Setup: If you want to run both Windows and Linux (or any combination of OSes) on the same computer, you'll need to create partitions for each system.
Organizing Personal and Work Data: Keeping work documents and personal media on separate partitions makes data management easier and reduces the risk of accidentally deleting important files.
Backup and Recovery Planning: Having a dedicated partition for backups (rather than an external drive) ensures critical files are isolated from the operating system.
Preparing New Drives: When adding a new SSD or HDD, you need to partition and format it before use.
Partitioning is generally safe when done properly, but mistakes happen. Common risks include:
• Data Loss from Mistakes: Accidentally deleting or formatting the wrong partition will erase your files instantly.
• Partition Table Corruption: Rare but serious power failures or software crashes during partitioning can corrupt the partition table, making the disk unreadable.
• Boot Issues: If you modify system partitions incorrectly, your OS may fail to boot.
Best Practices for Safely Partitioning a hard drive
✔️ Always back up your important files before making any changes.
✔️ Double-check which disk and partition you're working with especially when using command-line tools.
✔️ If you're unsure, start with built-in GUI tools before trying advanced software.
✔️ Use stable and reputable tools avoid outdated or unmaintained software.

DiskGenius is a one-stop solution to recover lost data, manage partitions, and back up data in Windows.
Download